Understanding Blockchain Technology in Finance
Learn how blockchain technology is revolutionizing financial transactions and security.
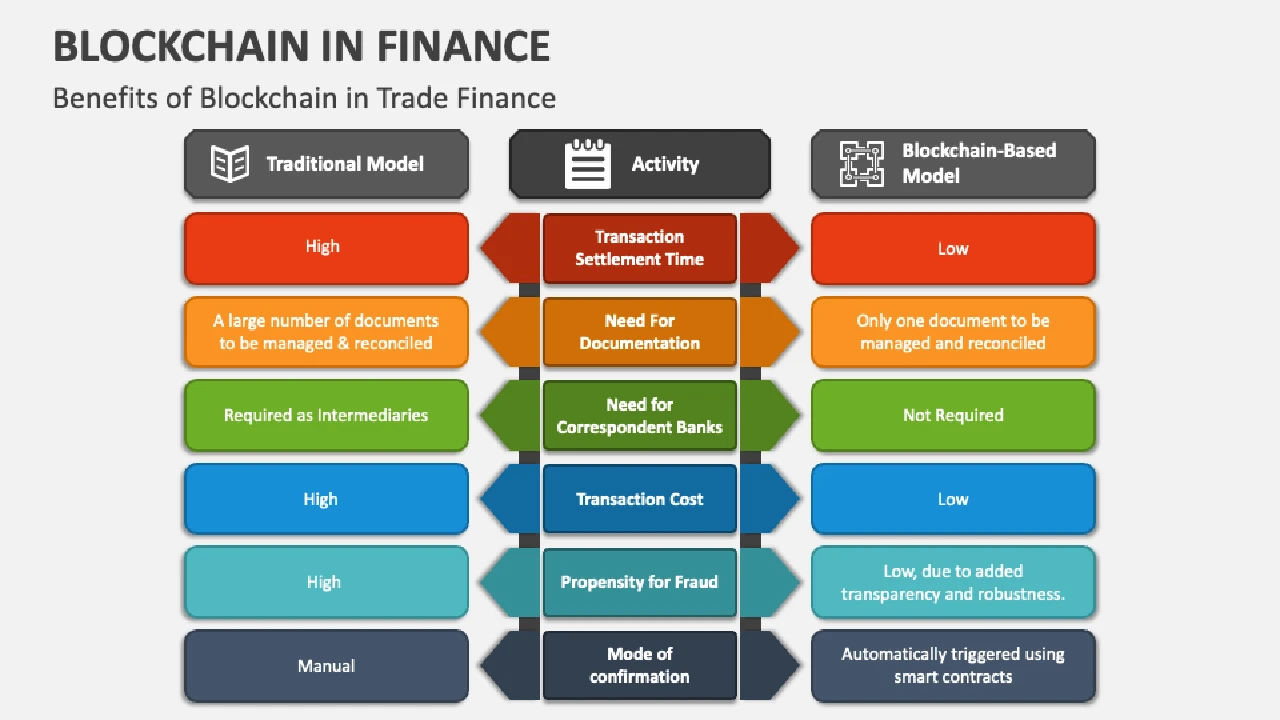
Understanding Blockchain Technology in Finance
What is Blockchain Technology A Core Concept Deep Dive
Alright, let's get down to brass tacks. You've probably heard the buzz about blockchain, especially with all the cryptocurrency talk. But what exactly is it? Think of blockchain as a super secure, decentralized digital ledger. Instead of one central authority like a bank keeping all the records, a blockchain distributes these records across a vast network of computers. Each 'block' in the chain contains a list of transactions, and once a block is filled, it's added to the chain, creating a permanent and unchangeable record. This immutability is a huge deal because it means once a transaction is recorded, it can't be altered or deleted. It's like a digital fingerprint for every piece of data.
The 'decentralized' aspect is key here. No single entity controls the entire network. This makes it incredibly resilient to attacks and censorship. If one computer goes down, the network keeps running because thousands of others are still active. This distributed nature also fosters transparency. While individual identities might be pseudonymous, the transactions themselves are visible to everyone on the network. This level of transparency, combined with the security of cryptographic hashing, makes blockchain a game-changer for trust and verification.
How Blockchain Works The Mechanics Behind the Magic
So, how does this digital ledger actually function? It all starts with a transaction. Let's say you want to send some cryptocurrency to a friend. That transaction is bundled with other recent transactions into a 'block.' Before this block can be added to the chain, it needs to be validated by the network's participants, often called 'miners' in the context of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. These miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to verify the transactions. This process is called 'Proof of Work' (PoW) or 'Proof of Stake' (PoS), depending on the blockchain.
Once a miner successfully validates a block, it's broadcast to the entire network. Other participants then verify the solution, and if everything checks out, the new block is added to the existing chain. Each new block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure and unbreakable link. This chain of hashes is what makes it so difficult to tamper with past transactions. Any attempt to alter a block would change its hash, invalidating all subsequent blocks and immediately alerting the network to the fraud. It's a self-correcting, self-securing system.
Blockchain in Finance Revolutionizing Transactions and Security
Now, let's talk about where blockchain really shines: finance. Traditional financial systems are often slow, expensive, and prone to errors due to multiple intermediaries. Blockchain offers a way to streamline these processes, making them faster, cheaper, and more secure.
Faster Cross-Border Payments and Remittances
Imagine sending money across continents in minutes, not days. Blockchain-based payment systems can cut out the numerous banks and clearinghouses involved in traditional international transfers. This means lower fees and quicker settlement times. Companies like Ripple (XRP) are already working with financial institutions to facilitate these types of payments. For instance, RippleNet is a network that uses XRP as a bridge currency to enable real-time, low-cost international payments. It's designed for banks and payment providers, offering a significant upgrade from the traditional SWIFT system. While not a direct consumer product, its underlying technology impacts the speed and cost of remittances globally.
Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
The immutable nature of blockchain makes it incredibly difficult for fraudsters to alter records. Every transaction is cryptographically secured and permanently recorded. This can significantly reduce fraud in areas like identity verification, insurance claims, and supply chain finance. For example, IBM Blockchain Platform offers solutions for supply chain transparency, helping track goods from origin to destination, reducing counterfeiting and ensuring authenticity. While not a consumer product, its enterprise applications directly enhance financial security for businesses and, by extension, consumers.
Decentralized Finance DeFi and Its Impact
DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, is a huge area where blockchain is making waves. It's about building financial applications on blockchain networks, removing the need for traditional banks and financial institutions. Think of lending, borrowing, trading, and insurance, all happening directly between users through smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Platforms like Aave and Compound allow users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies, earning interest or paying interest, all without a bank in the middle. These platforms are typically accessed via crypto wallets like MetaMask (free browser extension and mobile app) or Trust Wallet (free mobile app). The user experience can be complex for beginners, but the potential for financial inclusion and efficiency is enormous.
Tokenization of Assets Real World Assets on Blockchain
Blockchain allows for the 'tokenization' of real-world assets, meaning ownership of things like real estate, art, or even company shares can be represented as digital tokens on a blockchain. This can make these assets more liquid, easier to transfer, and more accessible to a wider range of investors. Imagine buying a fraction of a high-value painting or a commercial building. Platforms like Polymath aim to facilitate the creation and management of security tokens, making it easier for companies to issue tokenized securities. This is still an emerging area but holds immense promise for democratizing investment.
Comparing Leading Blockchain Platforms for Financial Applications
Not all blockchains are created equal. Different platforms are designed for different purposes, and their suitability for financial applications varies. Let's look at some of the big players:
Ethereum The Smart Contract Powerhouse
Ethereum is arguably the most popular blockchain for building decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. Its native cryptocurrency is Ether (ETH). Many DeFi protocols, NFTs, and enterprise blockchain solutions are built on Ethereum. It's highly programmable and has a massive developer community. However, it can suffer from high transaction fees (gas fees) and network congestion, especially during peak times. The recent transition to Ethereum 2.0 (now called the Merge) aims to address scalability and energy consumption issues by moving from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake. For developers, tools like Truffle Suite (free, open-source development environment) and Remix IDE (free, web-based IDE) are commonly used. For users, interacting with Ethereum dApps often requires a wallet like MetaMask (free).
Solana The High-Performance Contender
Solana is known for its incredibly high transaction throughput and low fees, making it a strong competitor for applications requiring speed and scalability. It uses a unique 'Proof of History' consensus mechanism combined with Proof of Stake. Many DeFi projects and NFT marketplaces have chosen Solana for its performance. However, it has faced some network stability issues in the past. Its native cryptocurrency is SOL. Developers often use the Solana SDK (free, open-source) for building applications. Wallets like Phantom (free browser extension and mobile app) are popular for Solana users.
Binance Smart Chain BSC The EVM Compatible Alternative
Binance Smart Chain (BSC), now part of the BNB Chain, gained popularity due to its compatibility with Ethereum's Virtual Machine (EVM) and significantly lower transaction fees. It's a centralized blockchain managed by Binance, which offers speed and cost-effectiveness but sacrifices some decentralization. Many DeFi projects and games have launched on BSC. Its native token is BNB. Developers can use similar tools as Ethereum, and wallets like MetaMask can be configured to connect to BSC.
Cardano The Research-Driven Blockchain
Cardano focuses on a research-driven approach, emphasizing peer-reviewed academic research in its development. It aims to provide a more secure and scalable platform for dApps and smart contracts, using a Proof of Stake consensus mechanism called Ouroboros. Its native cryptocurrency is ADA. While development has been slower than some competitors, its methodical approach appeals to many. Wallets like Daedalus (desktop wallet) and Yoroi (browser extension and mobile app) are used for Cardano. Development tools include the Cardano Node and Plutus Platform (for smart contracts).
Hyperledger Fabric Enterprise Grade Blockchain
Unlike the public blockchains mentioned above, Hyperledger Fabric is a permissioned blockchain framework, meaning participants need to be authorized to join the network. This makes it ideal for enterprise use cases where privacy and control are paramount, such as supply chain management, trade finance, and interbank settlements. It's not a cryptocurrency, but a framework for building private blockchain networks. Companies like IBM offer services around Hyperledger Fabric. There's no 'price' for the platform itself as it's open-source, but implementation and maintenance costs for enterprises can be significant. It's a B2B solution, not a consumer product.
The Future of Finance with Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is still evolving, but its potential to reshape the financial landscape is undeniable. We're seeing a shift towards more transparent, efficient, and secure financial systems. From faster payments to new ways of investing and managing assets, blockchain is paving the way for a more inclusive and accessible financial future. While there are challenges to overcome, such as regulatory clarity and scalability, the innovation happening in this space is truly exciting. Keep an eye on how these technologies continue to integrate into our daily financial lives.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)






